SD Wan
Software-Defined Wide Area Networks (SD-WAN)
Software Defined Wide Area Network Topology
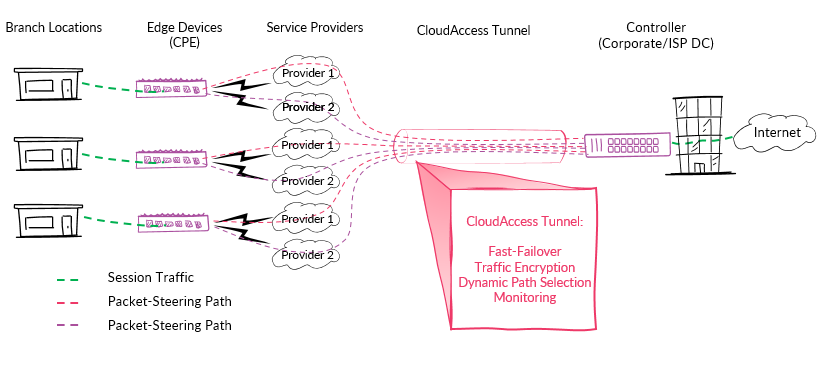
Cloud Access SD-WAN Innovation employs an integrated controller to intelligently direct traffic across the WAN. By optimizing traffic routing, users experience enhanced application performance across all branches. Each branch can have multiple internet connections for redundancy and bandwidth, along with features such as quality of service for application prioritization and encryption for secure data transmission.
The result? Increased business productivity, efficiency, and reduced IT costs.
SD-WAN Remote Control with an Orchestrator

Software Defined Wide Area Network – Alternative to MPLS
SD-WAN is a great alternative to MPLS because management and deployment can be configured remotely.
Analytics galore: Network alerts and link health monitoring

Why offer Cloud Access Software Defined Wide Area Networks?
Benefits of Cloud Access
- White Label – Brand it as your own
- Resides within the provider’s infrastructure
- Affordable hardware options
- Zero-touch deployment
- Remote configuration and management
- Bonded Internet Connectivity for increased bandwidth
- Backup Internet Connectivity for high availability
- Site-to-site encryption
-

